Reserve Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
Preauricular Incision Basics
Location
A preauricular incision is a surgical cut made just in front of (preauricular) the ear, along the natural crease or fold of skin.
It’s a common approach for various ear-related procedures, including:
• **Ear surgery (Otoplasty):** Used to reposition protruding ears, correct deformities, or reduce ear size.
• **Cholesteatoma removal:** A procedure to remove skin growths that can develop in the middle ear.
• **Hearing tube placement:
To drain fluid from the middle ear and improve hearing.
The location of a preauricular incision is chosen for its anatomical advantages.
It allows surgeons to access the inner ear structures while minimizing visible scarring.
This incision typically heals well and leaves a faint scar that often blends with the natural contours of the ear.
Purpose
A preauricular incision is a surgical cut made just in front of the ear, along the natural crease or fold of skin in front of the external auditory canal (ear canal). This location offers several advantages for surgical procedures involving the face, head, and neck.
The primary purpose of a preauricular incision is its versatility. It serves as an access point for various surgeries, including:
*
Ear reconstruction or repair: This might involve correcting deformities, addressing injuries, or removing skin cancers from the ear.
*
Facial nerve surgery: The preauricular incision allows surgeons to access the facial nerve without disrupting the hairline or leaving visible scarring on the face itself.
Procedures involving salivary glands: This area offers a good route for accessing and operating on the parotid gland, which is located just in front of the ear.
*
Lymphatic drainage surgery: Surgeons might use a preauricular incision to remove lymph nodes or perform biopsies in the neck.
The advantages of a preauricular incision include:
• **Scar concealment:** The scar tends to be hidden within the natural folds of the skin, making it less noticeable.
• **Minimal disruption to surrounding structures:** Because the incision is located away from important facial nerves and vessels, it minimizes the risk of complications.
• **Favorable cosmetic outcome:** The relatively inconspicuous location of the incision often results in a pleasing cosmetic result.
Types
A preauricular incision is a surgical cut made in front of the ear, within the natural crease of the skin.
This type of incision is often used for various ear-related surgeries, including:
- Earlobe repair:** To correct torn or elongated earlobes.
- Chondrodermatoplasty: To reshape or reconstruct the cartilage and skin of the ear.
- Otoplasty (ear pinning):**
To reposition protruding ears.
The incision is typically made using a scalpel, creating a clean and precise cut. The wound edges are then meticulously closed with sutures or staples to minimize scarring.
Types of Preauricular Incisions:
- Straight incision:** A single straight line is made across the front of the ear. This is often used for simple procedures, such as earlobe repair.
- Curved incision:** A curved cut follows the natural contours of the ear crease, creating a less noticeable scar.
The choice of incision type depends on the specific surgical procedure and the surgeon’s preference.
Generally, preauricular incisions are considered to be relatively low-risk and result in minimal scarring due to their placement within the natural skin folds.
Surgical Considerations
Book a Dermal Filler Consultation at It’s Me and You Clinic with Dr. Laura Geige
Procedure Details
A preauricular incision is a surgical cut made in front of (pre-) the ear (auricle). This type of incision is commonly used for various otolaryngological procedures, particularly those involving the external ear.
Surgical Considerations:
- Location: The precise location of the preauricular incision is carefully chosen based on the specific procedure and patient anatomy. It’s often made along a natural crease or line in front of the ear, minimizing visibility.
- Skin Tension Lines: Surgeons aim to make the incision along skin tension lines to promote healing and minimize scarring. Incisions perpendicular to these lines can lead to increased tension and poor wound closure.
- Accessibility: The preauricular approach provides access to the external ear structures, including the cartilage, perichondrium (tissue surrounding cartilage), and underlying muscles.
- Nerve Proximity: The facial nerve branches are located near the ear. Surgeons must meticulously avoid these nerves during incision placement and dissection to prevent facial weakness or paralysis.
Procedure Details:
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is typically used for preauricular incisions, but general anesthesia may be required for more complex procedures.
- Incision: The surgeon makes a precise incision in the chosen location.
- Dissection: The surrounding tissue and cartilage are carefully dissected to expose the targeted structures.
- Procedure Specific Steps: Depending on the reason for surgery, additional steps may be taken. This could involve:
- Reshaping or removing ear cartilage
- Removing skin tags or cysts
- Repairing ear defects
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures or staples. Depending on the procedure, a drain may be placed to remove fluid.
Recovery typically involves pain management, keeping the incision clean and dry, and avoiding strenuous activity for a period of time.
Risks and Complications Post-operative Care
A preauricular incision is a surgical cut made just in front of (pre- to) the ear, within the natural crease that forms between the skin and the cartilage. This location is chosen for its aesthetic appeal, as the scar typically fades well and blends in with the surrounding folds.
Surgical Considerations:**
The decision to use a preauricular incision depends on the specific surgical procedure being performed. It’s commonly used in:
- **Ear Reconstruction:** Repairing congenital deformities or traumatic injuries to the ear.
- **Otoplasty (Ear Pinning):** Correcting prominent ears by altering their shape and position.
Other factors influencing incision choice include:
- Size and location of the surgical area
- Patient’s individual anatomy and skin characteristics
- **Infection:** The risk of infection is present with any surgical incision.
- **Bleeding:** Surgical procedures may involve blood vessels, increasing the possibility of bleeding.
- **Scarring:** While preauricular incisions aim for minimal scarring, some degree of visible scar tissue may remain.
- **Nerve Damage:** Nerves located near the ear can be susceptible to injury during surgery, potentially causing temporary or permanent numbness.
- **Hematoma:** A collection of blood under the skin can form, requiring drainage and monitoring.
- Wear a protective dressing to promote healing and minimize swelling.
- Take prescribed pain medication as needed for discomfort.
- Apply cold compresses to reduce swelling.
- Avoid activities that strain the ears or put pressure on the incision site.
- Keep the incision clean and dry, following their surgeon’s instructions for wound care.
- First few days:**
- Week 1-2: The wound begins to close, and the swelling gradually subsides.
- Week 3-4: Most of the initial healing is complete, but the incision may still be tender.
- 6-8 weeks:**
- Functional Improvement:**
- Cosmetic Enhancement:
- Infection:
- Scarring:
- Bleeding or hematoma:
- Nerve damage:
-
Initial Pain and Swelling: Expect some pain, swelling, and tenderness around the incision site in the first few days after surgery. This is normal and can be managed with prescribed pain medication.
-
Dressing Changes: Your surgeon will provide instructions on how to care for the incision, which may involve changing dressings regularly. Keep the area clean and dry as directed.
-
Activity Restrictions: You’ll likely be advised to limit strenuous activity and avoid contact sports for several weeks to allow the incision to heal properly.
-
Follow-up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your surgeon to monitor healing progress and address any concerns.
-
Follow your surgeon’s instructions for incision care meticulously.
-
Protect the area from sun exposure during the healing process and always use sunscreen afterward.
-
Consider using silicone gel sheets or scar massage techniques as directed by your doctor to improve the appearance of the scar over time.
**Risks and Complications:**
As with any surgery, preauricular incisions carry potential risks and complications:
**Post-operative Care:**
Following surgery with a preauricular incision, patients typically:
Reserve Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Now
Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon are crucial to monitor healing progress, address any concerns, and ensure proper recovery.
Recovery and Outcomes
Expected Healing Time
Recovery and outcomes following a preauricular incision depend on several factors, including the complexity of the procedure, the individual’s overall health, and adherence to post-operative care instructions.
Expected Healing Time
Generally, the healing process after a preauricular incision takes several weeks:
**Outcomes**
Most individuals who undergo preauricular incisions experience a positive outcome, with effective removal of the cyst or other abnormality.
**Potential Complications**
While generally safe, there are potential complications associated with any surgical procedure:
Scarring
Recovery after surgery involving a preauricular incision typically involves a period of healing and potential discomfort. Understanding the process and following postoperative instructions carefully can aid in a smoother recovery.
Here’s what you can expect:
Scarring is a natural part of the healing process. The preauricular area has relatively good blood supply, which can promote healing and minimize scarring. However, some degree of scarring is inevitable.
To help manage scarring:
It’s important to remember that individual healing experiences can vary. Be patient and follow your surgeon’s guidance for optimal recovery and minimize scarring.
Long-Term Effects
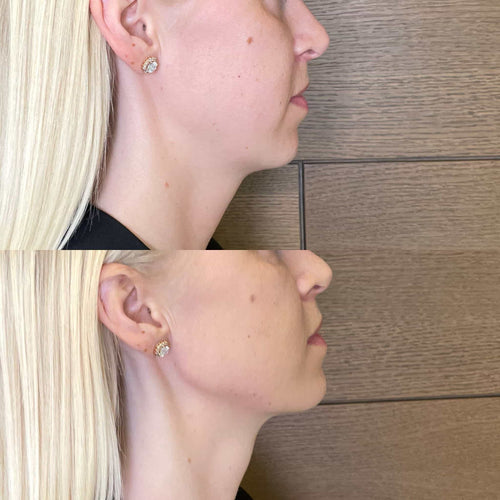
A preauricular incision is a surgical cut made in front of the ear, typically used during otoplasty (ear surgery) procedures.
The incision site allows the surgeon to access the cartilage and tissues behind the ear, making adjustments for reshaping or correcting deformities.
Recovery following preauricular incision surgery generally involves a period of rest, pain management, and wound care. Patients may experience swelling, bruising, and discomfort in the ear area, which typically subside within a few weeks.
The long-term effects of a preauricular incision are generally favorable.
The scar usually fades over time and becomes less noticeable.
However, some individuals may experience persistent mild scarring or a small indent at the incision site.
Overall, the benefits of preauricular incision surgery in achieving desired ear shape and aesthetics often outweigh the potential for minor long-term effects.
It’s important to consult with a qualified plastic surgeon to discuss the specific risks and benefits of this procedure and understand what recovery entails.
Aron Marquez Gifted Brits Making Memories London Josie Barrett Mocha Kid Magazine Ayiti Natives
- Why Do My Teeth Hurt After Lip Filler - November 8, 2025
- What Is The Best Procedure For Sagging Neck? - November 5, 2025
- What Are The Best CBD Gummies For Mental Focus And Clarity - November 4, 2025
